What are bifacial solar panels?
There are many reasons a home or business owner may be considering installing solar panels on their property. But generally, those who go ahead with the installation will have a common goal in mind: generating as much electricity as possible.
Solar panel technology has advanced leaps and bounds on what it used to offer. A particularly exciting development in the world of solar energy is the creation of bifacial solar panels, as opposed to traditional monofacial panels. What is a bifacial solar panel, you ask? And, are bifacial solar panels better than monofacial solar panels?
Well, you’re in the right place – read on to find out more.
What are bifacial solar panels?
Although bifacial modules have been around for quite a while (dating back as early as the sixties), there was little commercial interest in the technology until very recently. Now, thanks to the development of passive emitter rear cell (PERC) technology, bifacial modules have been gaining popularity within the solar market.
Solar panels are typically made up of one of two different types of cells: monocrystalline or polycrystalline — the vast majority of bifacial solar panels are made up of the former. While monocrystalline cells may be more expensive to manufacture and purchase, they offer greater efficiency in absorbing light for conversion to solar energy.
The main difference between the two types of solar panel is the method of manufacturing and construction. Traditional monofacial panels have an opaque backsheet, meaning that only the front-facing panel of cells is exposed to sunlight. However, bifacial panels include reflective, dual panes of glass securing the solar cells in place – meaning that the backs of the cells are also exposed to sunlight.
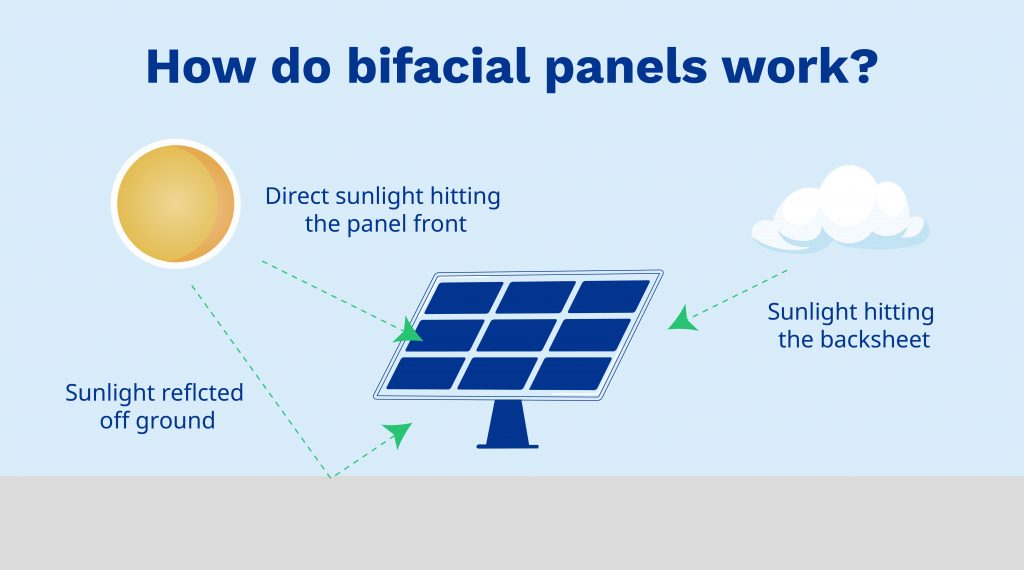
How do bifacial panels work?
Whereas monofacial solar panels can only produce power using the front of the panels, bifacial solar panels can produce power using both sides. This simple structural difference is what makes bifacial panels so unique, and often more beneficial to property owners.
To generate energy using both sides of the solar panel, bifacial panels either have a reflective backsheet or dual panes of glass (rather than the opaque ones found in traditional solar PV systems). Because of the reflection, energy production can now happen on both sides of the panel, increasing the overall energy efficiency of the module. This is excellent news for homeowners, who can expect more energy to be delivered to the property than with a conventional PV system.
To maximize the efficiency of bifacial solar panels, it’s important to consider their positioning. For example, the higher a bifacial panel is tilted, the more power it’s able to produce because reflected light can reach more of the cells on the back of the panel. Bifacial panels work well wherever the panels can be tilted to get the best exposure, as well as the most amount of reflected light – this includes both flat rooftops and ground-level surfaces. Dual-axis trackers can also be used to help promote flexibility and ensure the solar panels are getting the most sunlight possible during the day.
However, given that the power production of a bifacial solar panel’s backsheet mainly depends on the reflection of light, the total production of power is easily impacted by environmental conditions. As a result, each panel may perform differently. However, microinverters have module-level MPPT, which helps to maximize the power production of every panel.
Are bifacial solar panels better than traditional systems?
Since bifacial solar panels are becoming more widely explored as an option for greener energy, it’s to be expected that property owners will want to know the benefits that they can deliver over traditional modules.
Although the exact amount of energy produced will depend on the environment, it’s believed that bifacial solar panels can generate up to 11% more energy than monofacial panels. Bifacial solar panels tend to perform best when installed on flat rooftops and near highly reflective surfaces, such as glass, sandy, or snowy areas.
While the front of the panel takes in most of the sunlight, the backs of the cells are still able to generate anywhere between 5-30% of the energy absorbed by the front. As a result, bifacial solar panels are considered to be more efficient in capturing sunlight for solar energy, since both sides of the solar cells are exposed.
Are there any disadvantages to bifacial solar panels?
There are two main disadvantages that property owners should consider when looking into installing bifacial solar panels.
Firstly, the initial cost of bifacial panels is much higher than that of monofacial panels. Due to the complex manufacturing process involved in actually producing the bifacial panels, it can end up costing up to 10% more than traditional PV systems.
Secondly, bifacial solar panels are heavier and installation requires a bespoke approach, as well as specialized equipment to ensure the homeowner will get the most out of the new system. This, in turn, means that installation costs are much higher than those associated with monofacial panels.
Although prices are expected to fall as demand increases, bifacial solar panels are currently much more expensive than conventional PV systems per watt.
