How floating solar panels save space –
and protect the environment too
One of the biggest barriers to adopting solar panels is space.
It’s not always easy finding a large, flat stretch of ground or roof where solar panels can be installed at an angle that lets them soak up the sun.
Which is why floating solar panels are becoming increasingly popular. Installing floating solar panels on a large body of water like a lake or reservoir – one that isn’t used for recreational purposes, of course – is a great way to use space effectively.
In fact, floating solar panels might even outperform ground- or roof-mounted solar panels.
The future of solar might just be on the water.
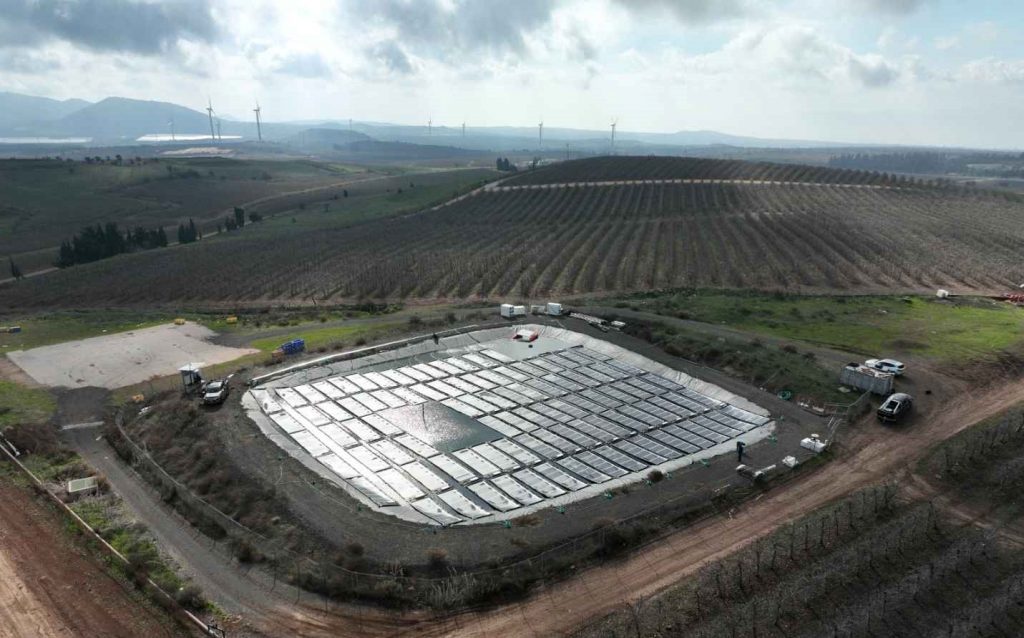

What are floating solar panels?
The clue really is in the name: Floating solar panels (sometimes called floating photovoltaics or “floatovoltaics”) are solar panels that float on a body of water.
They’re usually found on non-recreational lakes, reservoirs, or industrial ponds. There are even some offshore floating solar farms – albeit ones that are relatively close to land.
Floating PV systems are generally designed in the same way as traditional solar systems: All of the same solar power technology is simply attached to a series of polyethylene floats to keep the panels above water.
Tethers are used to keep the panels from drifting away and ensure they’re angled towards the sun. These tethers also make it easy to drag the solar panels to a new position if, for example, bad weather makes the water choppy or the surface level of the water changes.
Floating solar panels have been around for a while, but they’re only just starting to become popular; in 2022, they only made up about 2% of solar installations worldwide.
However, if floating solar panels continue to grow in popularity, they could have an enormous impact on the environment. Some research shows that, if just 30% of global reservoirs were covered with floating solar panels, they would generate enough energy to power 62,000 cities – twice the amount of power used by the US annually.
Why are floating solar panels used?
It takes a lot of space to generate solar power on a large scale. Much more space than some businesses can justify.
Solar power might be exponentially more sustainable than fossil fuels, but it demands much more land. Natural gas, for example, is around 80 times more power-dense than solar power.
Solar systems generate the most power when they’re placed on wide, flat stretches of ground that get a lot of sunlight.
Luckily, these kinds of conditions are relatively easy to find.
Unluckily, they’re the exact same conditions that make great farmland – meaning these spaces are often already being used for crops, or would be much more profitable if they were used for farming in the future.
Even if there is enough unused space available to build a solar farm, large-scale solar systems can have unexpected effects on their surrounding environment. For example, many large solar systems require forests to be cleared or affect conservation efforts intended to improve biodiversity.
Deserts seem like perfect places to build solar farms: they’re usually flat, empty, and flooded with sunlight. But recent research suggests that solar panels installed in the Sahara Desert might alter local temperatures and disrupt airflow, kicking off a chain reaction that could cause droughts in the Amazon or melt ice in the Arctic.
Floating solar systems could be the perfect solution to this problem.
What are the benefits of floating solar systems?
As solar floating solar systems become more common, it’s becoming clear that the benefits of “floatovoltaics” go way beyond just saving space on land.
Floating solar panels perform better (and the ROI is better, too)
It might sound counterintuitive, but solar panels actually perform better in lower temperatures. Which means most solar systems need to strike a careful balance between staying cool and catching as much sun as possible.
Floating solar panels on a large body of water actually helps to cool the panels – some studies suggest this could improve efficiency by 11% compared to land-based panels.
Floating solar panels are even better for the environment than land-based ones
By blocking the sun from hitting the surface of the water, floating solar panels reduce the amount of evaporation in lakes and reservoirs. If 30% of global reservoirs were covered in solar panels, research estimates that they would save enough water to serve 300 million people each year.
And this effect isn’t limited to reservoirs of drinking water – floating solar panels on the surface of a hydroelectric dam increases the amount of water that can be used for hydropower. Or solar panels on the surface of an industrial lake can save water for irrigating farmland.
The extra shade also helps reduce the chance of algae blooms, which can be very dangerous for humans as well as plants and animals that live in the water.
Floating solar arrays cut down on carbon emissions
We’ve already talked about how floating solar panels reduce evaporation and how they can be installed without cutting down trees or disrupting global airflow.
But they’re really powerful as a way to multiply the benefits of hydroelectric dams.
Hydroelectric power is renewable, but running a hydroelectric power plant can be carbon intensive. However, installing floating solar panels in the lake of a hydroelectric dam provides a clean, easily used source of electricity that can help to offset the plant’s emissions.
Some floating solar systems can be amazing for tourism
Floating solar systems can be very beautiful to look at – just take a look at pictures of the world’s biggest solar farm in Ubon Ratchathani, Thailand.
Not only does the installation reduce Thailand’s carbon emissions by 47,000 tonnes each year, but it’s also set to become a major tourist attraction. Officials built a 415-meter long “Nature Walkway” alongside the dam, allowing tourists to walk alongside the water and take in the arrangement of shimmering panels.
What are the challenges of installing floating solar panels?
So, floating solar panels can be an excellent way to generate large amounts of power without eating up space on land or reduce their negative impact on the local environment.
But there are a few challenges that can make installing them tricky:
- The environment can be harsher. When you float solar panels on the water, you need to think about a whole range of potentially damaging forces that aren’t much of a problem on land. High wind speed, water erosion, and contaminants in the water can affect both the solar panels and the inverters that come with them. This means that all of the components of the solar system need to be carefully chosen and made from materials that can withstand the elements.
- They could harm aquatic life. If floating solar panels can kill off algae, they could also kill off other, friendlier forms of life. It’s not just that solar panels block out light; the tethers and flotation devices could also injure any animals living in the water. That’s why floating solar systems should only ever be installed on man-made lakes and reservoirs that have little to no wildlife living in them. Operators should also take care to regularly check up on any wildlife living in the water to ensure that it’s not suffering from any negative effects.
- The installation site needs to be chosen carefully. Being able to install solar panels on water certainly opens up a whole new range of potential sites – but they can’t be installed just anywhere. Installers will need to check the wind speeds, how much the water rises and falls, the flora and fauna living in the water, and a wide range of other factors before they can begin construction.
- They can take longer to install. And not just because installers need to spend a long time checking all the things we covered in the previous bullet point. The mooring and anchoring systems in floating PV systems are quite complex and take time to install. Not to mention that installing any electrical equipment in water can be dangerous if it’s not handled with care and attention; installers will need to take strict electrical safety precautions at all times.
How can Hoymiles help with your floating solar system?
In the next few years, floating solar panels are probably going to go from being quite rare to being the norm all over the world. And no wonder: They cut out lots of the drawbacks of land-based solar system and provide some extra benefits of their own too.
But they’re definitely harder to install and maintain than traditional solar panels – which means that, if you want to get the most out of them, you’ll need to choose every component of your system very carefully.
At Hoymiles, we’re known around the world for reliable, robust microinverters. Microinverters that not only convert solar energy from DC to usable AC power with incredible efficiency but which are also built to hold up against the elements.
Hoymiles microinverters are:
- IP67 rated, and built to resist both water and damaging solids like dirt and debris. Crucially, all of our microinverters are compliant with corrosion resistance standards like ISO 9223:2012, and are classified as C5 “very high” anti-corrosivity – so you can have complete confidence in their performance, whether your solar system is installed inland or near the coastline.
- Built with aluminium alloy covers and a durable powder coating, designed to withstand anything the world – or the water – can throw at them.
- Tested thoroughly – we even put them through a 500-hour salt spray test to make sure they can survive in seawater too. We also test their performance in a variety of environments, including temperate and subtropical zones and atmospheric environments with very high pollution or chloride concentrations (such as industrial areas, coastal areas, and sheltered positions on coastlines).
- Designed to work underwater as well as above the surface.
In fact, our microinverters are already delivering results at a 300 kW floating solar system in Israel, providing outstanding efficiency and total reliability every day.
So if you’re ready to start reaping the benefits of floating solar panels, get in touch – our world-leading technology is ready to help.
